WaterSpaltting produces an unrealistic appearance with severe color over-saturation, especially noticeable in the color chart regions. In contrast, our SeaFree-GS reconstructs a more faithful scene appearance with balanced and realistic colors, with no over-saturation as seen in WaterSpaltting.
Reconstructing underwater 3D scenes with accurate appearances is crucial for numerous tasks. However, existing underwater 3D reconstruction methods often fail to restore the true scene appearance due to degradation in underwater images caused by water effects.
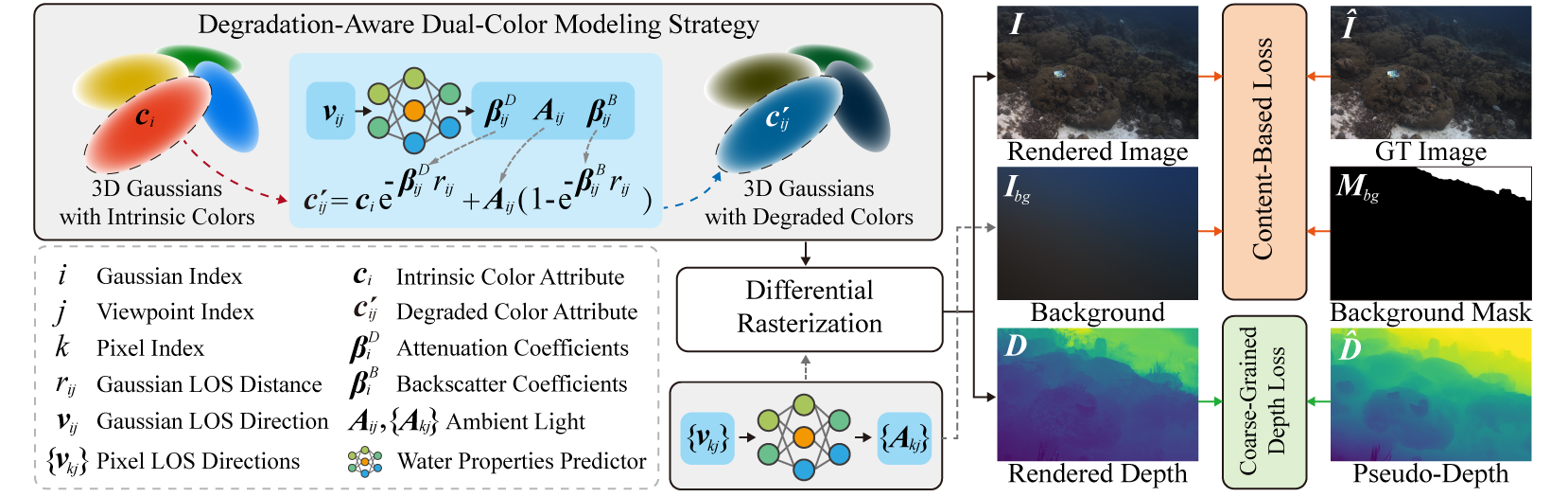
In this letter, we propose SeaFree-GS, a novel approach leveraging 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to reconstruct underwater scenes with their true appearances. Specifically, we introduce a Degradation-Aware Dual-Color Modeling strategy, where each Gaussian is assigned an intrinsic color representing the true scene appearance and a viewpoint-dependent degraded color to incorporate water effects. For a given viewpoint, this strategy physically derives the corresponding degraded colors from the intrinsic colors to render the underwater image. To improve reconstruction accuracy, we introduce a Content-Based Loss for selective enhancement of supervision over foreground and background regions, and a Coarse-Grained Depth Loss to enforce additional geometric constraints.
Experiments on three datasets demonstrate that SeaFree-GS achieves state-of-the-art performance in Underwater True Appearance Reconstruction, and also performs competitively in Underwater Novel View Synthesis.
Below, you can choose different scenes to view the rendering results of our SeaFree-GS on different downstream tasks. The left part of the videos shows the true scene appearance reconstructed by SeaFree-GS, free from water effects, i.e., the result of performing the Underwater True Appearance Reconstruction (UTAR) task. The right part of the videos shows the underwater imaging result rendered by SeaFree-GS under the influence of water effects, i.e., the result of performing the Underwater Novel View Synthesis (UNVS) task. Please select a scene from the dropdown menu:
Here, you can view the comparison of SeaFree-GS (right part) with the SOTA method, WaterSpaltting (left part), for the Underwater True Appearance Reconstruction (UTAR) task. While WaterSpaltting suffers from color over-saturation in the reconstructed scene appearance, SeaFree-GS reconstructs a more realistic and reliable scene appearance with natural colors. Please select a scene from the dropdown menu to explore different results.
This section showcases the comparison of SeaFree-GS (right part) with WaterSpaltting (left part) for the Underwater Novel View Synthesis (UNVS) task. While our SeaFree-GS primarily focuses on reconstructing the true appearances of underwater scenes, it also demonstrates competitive performance in integrating water effects and rendering degraded underwater images compared to the SOTA method, WaterSpaltting. Please select a scene from the dropdown menu to explore different results.